In the era of big data, everyone is aware of the importance of analytics. But actually doing big data analytics can be challenging, and it often happens only after the fact.
Many companies simply dump all of their data into their relational databases of choice and then leave it there. They may do batch processing of historical data every month, quarter, or do some other after-the-fact data analysis.
Dumping everything into data storage and occasionally doing some descriptive analytics may technically qualify as big data analytics. But the point of any kind of data analytics is really to obtain actionable insights. If you’re only looking at your data after the fact, you can miss a lot.
But there’s an answer: real-time analytics.
What is Real-Time Analytics?
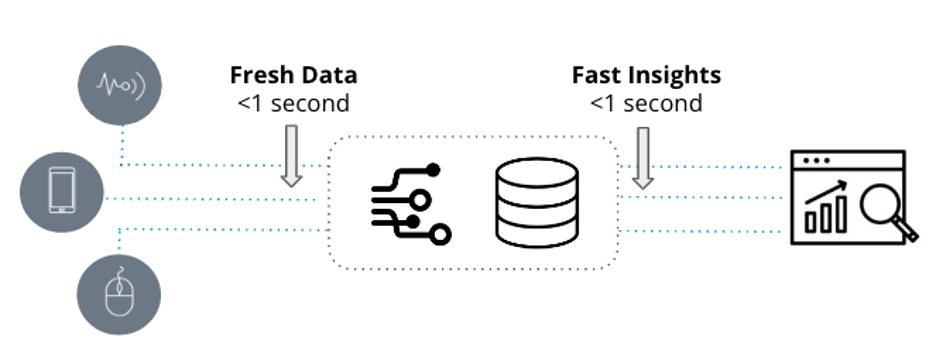
Real-time analytics, sometimes called streaming analytics or continuous analytics, is processing and analyzing data as it comes in, as close to real-time as possible.
The main advantage of real-time analytics is that it allows you to react quickly to changes and extract actionable insights from your data more quickly.
 Source: Splunk
Source: Splunk
Imagine, for example, that you’ve shipped a new version of your site, but a mistake in the code has caused the “purchase” button on your sales page to stop working.
With a properly-configured real-time analytics setup, you would discover and diagnose this pretty quickly, as real-time sales and that specific page’s conversion rate would drop to zero.
Without real-time analytics, it could take days or even longer to notice the change, costing you sales and user trust.
The main disadvantage of real-time analytics is that depending on how it is approached, setting it up can be difficult. Building a streaming data analytics system from scratch involves technical challenges beyond what it takes to do data analytics or data science.
 Source: Memgraph
Source: Memgraph
A data scientist, or even a team of data scientists, might not have the skills required to build such a system.
Building a system from scratch would involve expertise with data engineering, cloud computing, and technologies like AWS, possibly integrating functionality from services like Azure Stream Analytics or Amazon Kinesis to help with data stream processing, and potentially much more.
Who Uses Real-Time Analytics?
Simply put, companies recognize there’s often immense value in getting business intelligence quickly.
While it’s not necessary to monitor every metric in real-time or set up artificial intelligence systems to do continuous intelligence on all of your real-time data, there are areas in most businesses where real-time big data analytics offers real value.
For example:
- Web-based businesses can use real-time analytics to quickly identify and diagnose bugs, downed services, and other issues through real-time reporting on web analytics metrics, such as traffic.
- Banks and payment processors use real-time analytics to automate instantaneous fraud detection and prevent fraudulent purchases immediately.
- Marketing and Customer Satisfaction departments can use real-time analytics to more effectively target and serve the needs of specific users at that moment.
Companies in almost every industry make use of real-time analytics, although the depth of analysis may vary.
Some companies may use a simple real-time dashboard to track a few basic metrics. Others may build an advanced setup that’s pulling from dozens of data sources, doing data processing on the fly, and using machine learning for predictive analytics.
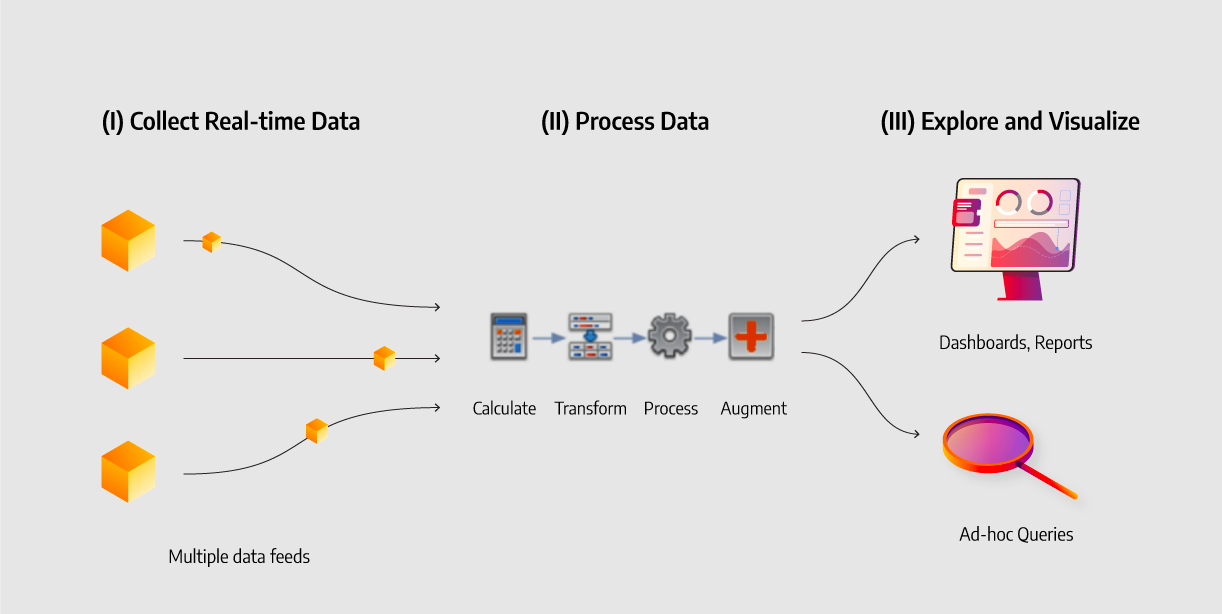
How Does Real-Time Analytics Work?
Real-time analytics systems typically work in one of two ways.
Truly real-time systems pull, analyze, and visualize data on the fly, as that data is being recorded and stored in the database.
 Source: Imply
Source: Imply
This is often called streaming data analytics because it involves working with the data stream as it’s generated rather than running a query against data already in the DB.
Other systems achieve near-real-time results by querying data that has already been stored in the database or a data warehouse at a regular interval — say, a few hours, or even a few minutes or seconds.
This is often called streaming data analytics because it involves working with the data stream as it’s generated rather than running a query against data already in the DB.
Other systems achieve near-real time results by querying data that has already been stored in the database or a data warehouse at a regular interval — say, a few hours, or even a few minutes or seconds.
This batch analytics approach does mean the data is analyzed slightly later, but it also reduces some of the technical challenges inherent in working with real time data analysis and may reduce cloud costs by consuming compute resources more efficiently.
Both approaches can be considered real-time data analytics.
As for many companies and use cases, there is not much practical difference between a streaming analytics system running a live analysis and a system that’s querying the database once a minute to run that same analysis.
In the real world, real-time analytics setups can differ dramatically from company to company. A company’s products, tech stack, cloud services, and requirements will all impact how it sets up its real-time data analytics systems.
In the context of web analytics, though, real-time analytics is often included as one of the features in many of the best web analytics tools. This may include the generation of real-time reports, as well as more advanced functionality, such as automation.
Examples of Real-Time Analytics
A simple example would be the real-time tab in Google Analytics that displays the number of visitors currently on your website. But let’s take a look at some more detailed, business-focused examples.
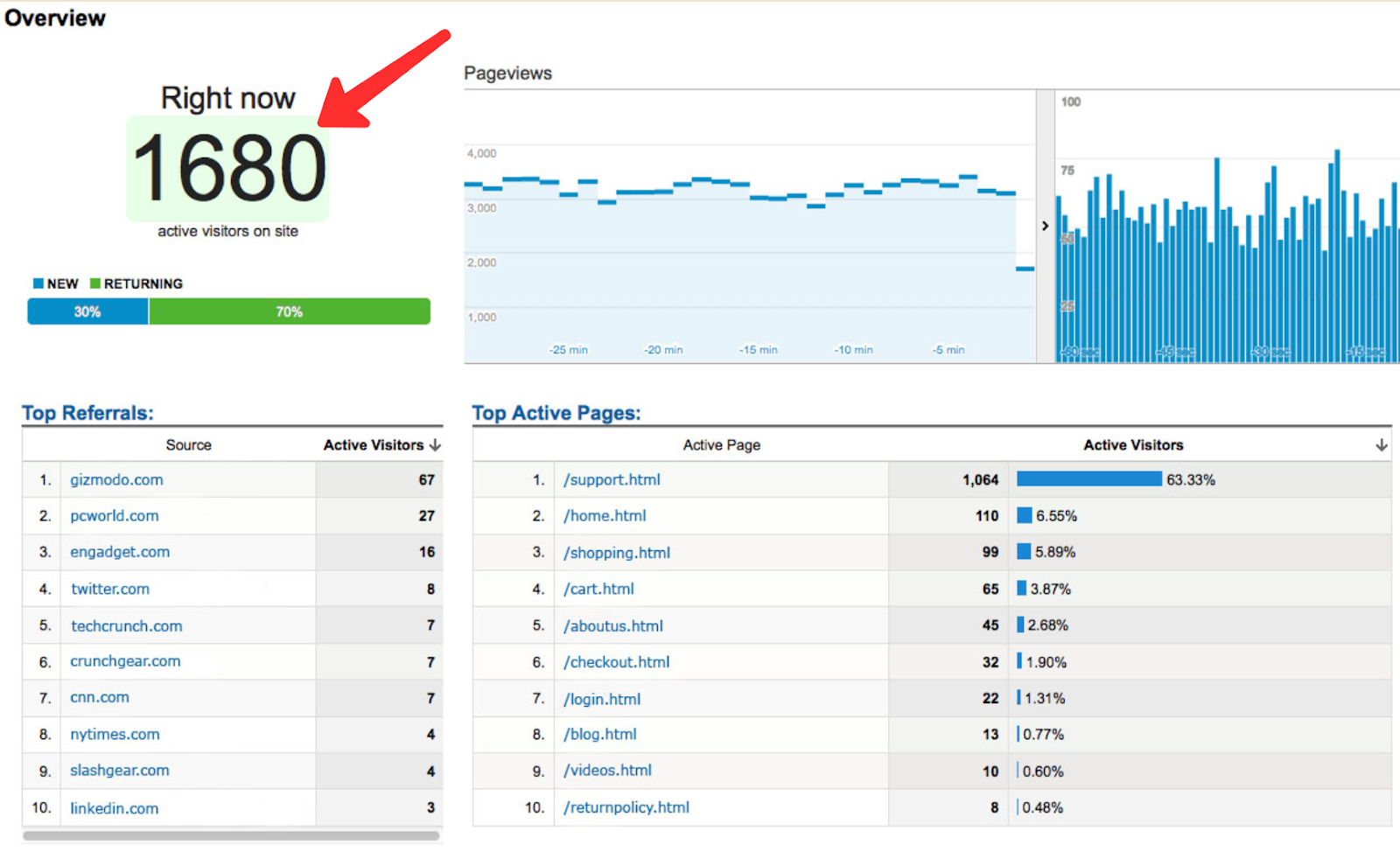 Source: Cardinal Path
Source: Cardinal Path
You could gain some decent insight from this data source and easily store it in Google Cloud. But let’s take a look at some more detailed, business-focused examples.
First, let’s look at an example of real-time analytics that would be quite easy to implement: Woopra. Woopra is in part a customer journey analytics tool, but it also offers web analytics features, including real-time analytics and real-time event-based triggers and automations.

For example, you could set up a trigger to send a welcome email and notify a salesperson immediately when a user with certain characteristics visits a specific page. This allows you to strike while the iron is hot, so to speak.
It also allows you to avoid the hassle of having to dig through your historical data, looking for customer behavior that suggests a particular user would be a promising lead. Why do all of that work manually, on a delay, when it can happen automatically and in real-time?
Real-time analytics can be used as described above, to take proactive steps or as a prescriptive analytics solution. It’s also a very valuable tool for reacting quickly to minimize damage when something has gone wrong.
For example, imagine a company with a fairly complex web page that’s reliant on a variety of open-source frameworks and APIs. When one of those APIs goes down, it will impact the company’s services, and potential users’ ability to even browse the site.
 Source: Mangools
Source: Mangools
However, the API provider may not inform all of its users about the outage. They may not even be aware of the outage themselves! If the company has a real-time data analytics setup, that monitoring may help them quickly find and identify the problem.
Shifting gears, imagine an assembly line that involves both human and robot workers. Having a real-time analytics set up to analyze the robots’ performance may help catch problems, bugs, and anomalies before they’re perceptible to humans.
This could help save on maintenance costs, but more importantly, it could help prevent serious accidents. No human could watch all of the robots and analyze every single action they take in real-time, but a big data analytics setup with streaming data processing could.
One final example of real-time big data analytics: financial trading. In global financial markets, seconds and even microseconds can cost huge sums of money, so trading companies invest in streaming data analytics systems that can process all kinds of data in real-time.
For example, If a stock’s price is rising, but the number of sell orders is also ticking up, being able to see and react to that information in real-time is valuable for human traders, and even more important for algorithmic traders (as speed is one of their primary advantages).
Real-Time Analytics Benefits
The primary benefit of any real-time analytics setup is speed. And as we’ve outlined in the examples above, the speed provided by real-time analytics tools can help with both proactive and reactive business strategies and can be useful for both manual and automated tasks.
At the end of the day, the technical implementation details and the specific metrics being measured may change, but there’s really no business or industry where uncovering insights quickly doesn’t offer tangible benefits.
Knowledge is power, and real-time analytics can help businesses get their hands on that knowledge faster. Being able to respond quickly to opportunities and react quickly to resolve problems pays dividends no matter what business you’re in.
Specifically, companies that set up real-time analytics systems may expect tangible benefits such as:
- Higher sales due to quicker user targeting and product recommendations.
- Shorter downtime due to the real time system quickly flagging anomalies and major changes in the data.
- Increased customer satisfaction as their needs are being met more quickly and accurately.
- A more empowered team that can view data and take action based on strong business intelligence without delay.
- Greater operational efficiency by processing data and implementing findings far quicker than using traditional analytics.
But of course, the specific benefits you can expect from real time analytics will depend on a lot of individual factors. Your business, product, tech stack, the metrics you’d like to track, and the types of analyses you’d like to perform will all play a role.
It’s also worth pointing out that real time user facing analytics can also be useful for A/B testing and iteration.
Particularly for companies with high-traffic websites, it’s possible to set up a split test and then use real time data analytics to quickly determine and implement whatever option won the test.
 Source: VWO
Source: VWO
The good news is that while real time analytics can be technically complicated when you’re building from scratch, there are plenty of tools out there to help companies that don’t want or need to go the bespoke route.
Particularly in the context of web analytics, there’s no need to reinvent the wheel. Excellent web analytics tools such as Woopra exist and already include support for real time analytics and automation, as well as intuitive data visualization.
Before fighting with Apache Spark and trying to figure out Spark streaming (or whatever technology you choose), it’s worth taking a serious look at the available plug-and-play solutions.
Particularly in the context of web and SaaS businesses, with a tool like Woopra, you’ll probably find that the key integrations from your existing tech stack are already supported, and it won’t take you long at all to get set up and start taking advantage of real time big data analytics.



